Craft art is the name of a craft that has long been rooted in the traditional Kazakh environment, producing art products of applied importance in the household and economic sphere.
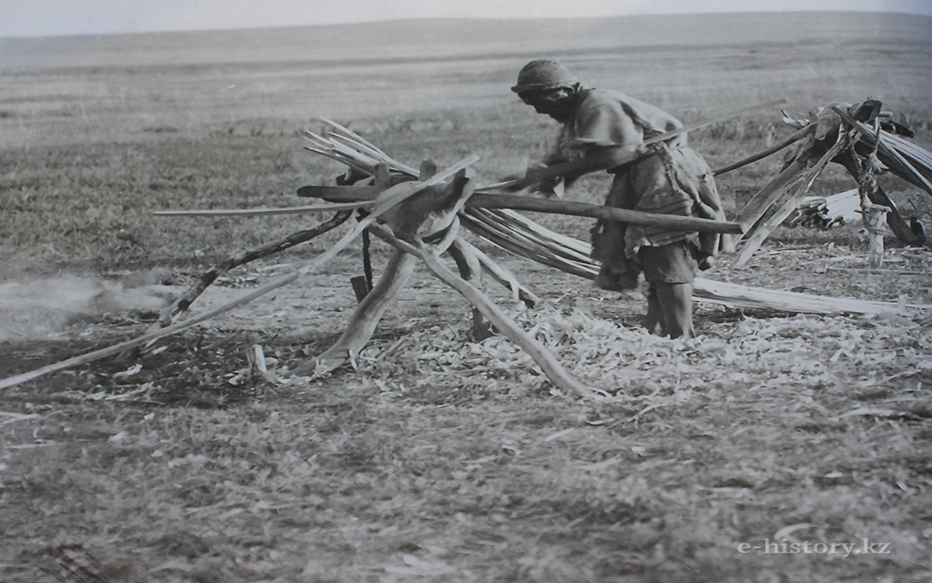 Crafts were formed and developed in direct connection with all branches of the nomadic life system. That is why they are multidisciplinary. Crafts in a nomadic society were not professionally classified as in a sedentary cultural environment. Due to the socio-economic and cultural characteristics of the traditional Kazakh environment, one master simultaneously performed several labor operations. There is a lot of information in historical and ethnographic data about the harmony of aesthetics and the practical significance of crafts.
Crafts were formed and developed in direct connection with all branches of the nomadic life system. That is why they are multidisciplinary. Crafts in a nomadic society were not professionally classified as in a sedentary cultural environment. Due to the socio-economic and cultural characteristics of the traditional Kazakh environment, one master simultaneously performed several labor operations. There is a lot of information in historical and ethnographic data about the harmony of aesthetics and the practical significance of crafts.
In Kazakh life, it was not customary to specify the exact price of handicrafts and sell them for money. The craftsmen worked to order. The price of an item varies from place to place and is set according to prevailing trends among the local population. There was no prior agreement, contract or bargaining between the master and the customer. They planned in advance the wages paid according to the established custom. Artisans could often use their salaries to buy goods in the form of horses, sheep, and wool.
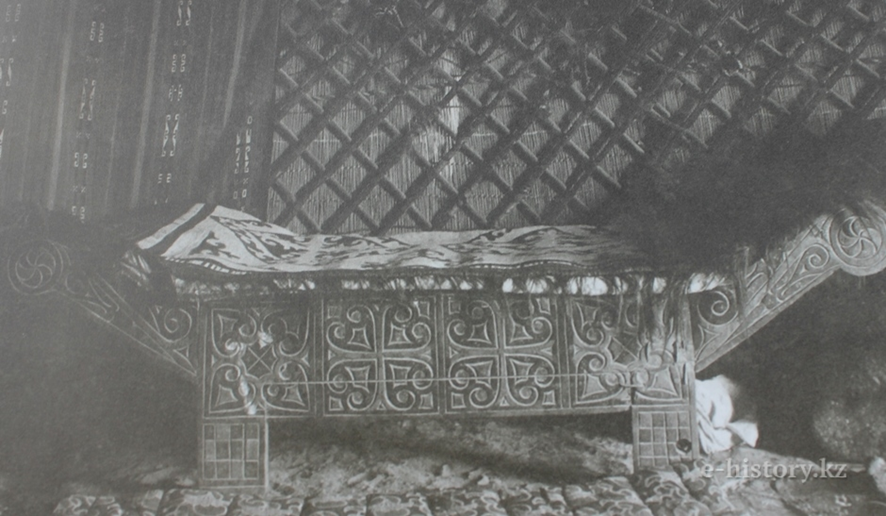

There are several branches of Kazakh crafts: home art, carpentry, axe making, blacksmithing, butchering, furniture making, horse riding, weaving, jewelry, leather, fur, shoemaking, stone work, carpet making, embroidery art, painting art, mat weaving, felting art. From some types of crafts, classification by profession follows, for example, a cartwright, a chest maker, a logger, a carpenter, a shanyrakshi ("a master who makes shanyrak"), a weaver, an ornamentalist, a konshi ("a master of working with leather"), a knutmaker, a tailor, a borikshi ("a master of sewing a headdress"), etc.
Depending on the gender of the people involved in crafts, they are divided into crafts that are practiced by men and crafts that are practiced by women. For example, men were engaged in processing wood, stone, clay, bone, horn, metal, leather and making various products from them.